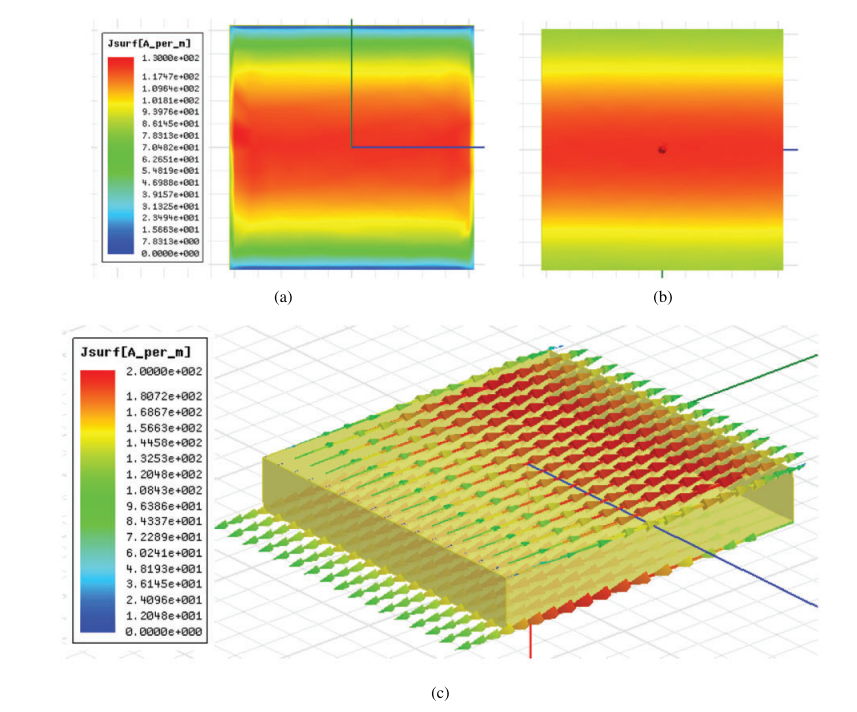
Abstract: A 5G wireless system requests a high-performance compact antenna device. This research work aims to report the characterization and verification of the artificial magnetic conductor (AMC) metamaterial for a high-gain planar antenna. The configuration is formed by a double-side structure on an intrinsic dielectric slab. The 2-D periodic pattern as an impedance surface is mounted on the top surface, whereas at the bottom surface the ground plane with an inductive narrow aperture source is embedded. The characteristic of the resonant transmission is illustrated based on the electromagnetic virtual object of the AMC resonant structure to reveal the unique property of a magnetic material response. The characteristics of the AMC metamaterial and the planar antenna synthesis are investigated and verified by experiment using a low-cost FR4 dielectric material. The directional antenna gain is obviously enhanced by guiding a primary field radiation. The loss effect in a dielectric slab is essentially studied having an influence on antenna radiation. The verification shows a peak of the antenna gain around 9.7 dB at broadside which is improved by 6.2 dB in comparison with the primary aperture antenna without the AMC structure. The thin antenna profile of λ/37.5 is achieved at 10 GHz for 5G evolution. The emission property in an AMC structure herein contributes to the development of a low profile and high-gain planar antenna for a compact wireless component.
 Keywords: AMC; metamaterial; planar antenna; high-gain antenna
Full paper : https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Pracha-Osklang/publication/364305729_Artificial_Magnetic_Conductor_as_Planar_Antenna_for_5G_Evolution/links/6344aa26ff870c55ce1661bd/Artificial-Magnetic-Conductor-as-Planar-Antenna-for-5G-Evolution.pdf
Keywords: AMC; metamaterial; planar antenna; high-gain antenna
Full paper : https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Pracha-Osklang/publication/364305729_Artificial_Magnetic_Conductor_as_Planar_Antenna_for_5G_Evolution/links/6344aa26ff870c55ce1661bd/Artificial-Magnetic-Conductor-as-Planar-Antenna-for-5G-Evolution.pdf
 Keywords: AMC; metamaterial; planar antenna; high-gain antenna
Full paper : https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Pracha-Osklang/publication/364305729_Artificial_Magnetic_Conductor_as_Planar_Antenna_for_5G_Evolution/links/6344aa26ff870c55ce1661bd/Artificial-Magnetic-Conductor-as-Planar-Antenna-for-5G-Evolution.pdf
Keywords: AMC; metamaterial; planar antenna; high-gain antenna
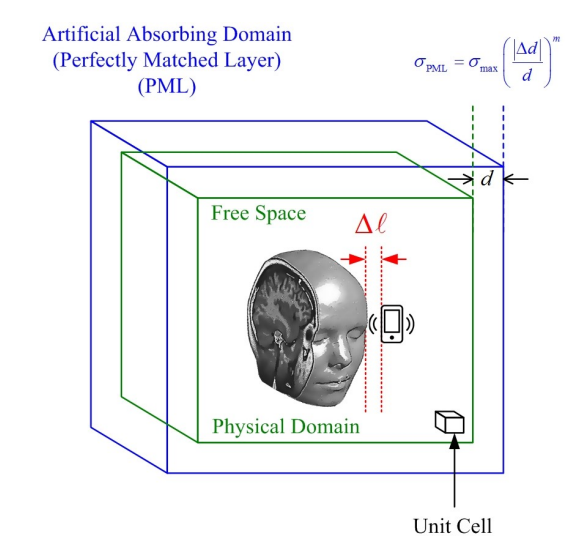
Full paper : https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Pracha-Osklang/publication/364305729_Artificial_Magnetic_Conductor_as_Planar_Antenna_for_5G_Evolution/links/6344aa26ff870c55ce1661bd/Artificial-Magnetic-Conductor-as-Planar-Antenna-for-5G-Evolution.pdfAbstract : This research work proposes a method to rigorously model a 3D human head from the informative data in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The approach is based on each slice of 53 MRI resized to a 64 × 64 grayscale image to enable a practical simulation. The optimized unit cell of 5.6 × 5.6 × 5.6 mm3 is identified as a particular type of tissue. It corresponds to the average size of an
actual human brain. The material properties are assigned to various tissues of the entire structure of the human head. The computational model of this will then be used as a virtual object to study the specific absorption rate (SAR) with electromagnetic radiation (EMR) at 2.6 GHz as a 5G mid-band frequency. A commonly known finite-different time-domain (FDTD) method is used as a
tool in the SAR simulation. The key results show that a handset with a power of less than 0.8 W, operating at a handset to head separation distance of 1.12 cm, will meet the FCC SAR 1g limit of 1.6 W/kg.
 Keywords: Rigorous Human Head Model, Finite-Different Time-Domain, FDTD, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, MRI, Specific Absorption Rate, SAR, Electromagnetic Radiation, EMR
Fill Paper : https://ph02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/ECTI-EEC/article/download/247522/167981/886057
Keywords: Rigorous Human Head Model, Finite-Different Time-Domain, FDTD, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, MRI, Specific Absorption Rate, SAR, Electromagnetic Radiation, EMR
Fill Paper : https://ph02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/ECTI-EEC/article/download/247522/167981/886057
 Keywords: Rigorous Human Head Model, Finite-Different Time-Domain, FDTD, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, MRI, Specific Absorption Rate, SAR, Electromagnetic Radiation, EMR
Fill Paper : https://ph02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/ECTI-EEC/article/download/247522/167981/886057
Keywords: Rigorous Human Head Model, Finite-Different Time-Domain, FDTD, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, MRI, Specific Absorption Rate, SAR, Electromagnetic Radiation, EMR
Fill Paper : https://ph02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/ECTI-EEC/article/download/247522/167981/886057Abstract: Coconut’s sweetness consistency has a close connection with the quality of coconut’s byproducts. And this is due to multiple factors. One of which is the maturity of coconut. Maturity classification is, therefore, the main concern for both consumers and manufacturers. However, currently the maturity classification process is mainly based on individual experience and skills developed throughout the time in the industry. Our research proposes an automatic maturity classification with a deep learning which could minimize the maturity classification time cost. The fully trained CNN structure with fine-tuning of transfer learning from well-known models were analyzed and compared. The experimental results showed that our proposed CNN structures achieved the best validation accuracy by 4-fold cross validation results with 97.27% with Binarized Saturation images, and 89.42% with HSV images.
 Keywords : Convolutional neural network, Coconut Classification, Deep learning
Full Paper : https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9454744/
Keywords : Convolutional neural network, Coconut Classification, Deep learning
Full Paper : https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9454744/
 Keywords : Convolutional neural network, Coconut Classification, Deep learning
Full Paper : https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9454744/
Keywords : Convolutional neural network, Coconut Classification, Deep learning
Full Paper : https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9454744/Abstract: A coconut is one of the most well-known fruit of Thailand as indicated by the Office of Agricultural Economics, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives and the national production volume of coconuts is significantly high as compared to other agricultural products. Particularly, in 2016 the value of the exportation of coconuts in Thailand is around 13,400 million baht [1]. At present, information technology plays a vital role as a driven force in various business environment. The technology is hence brought into various agricultural areas in order to efficiently improve the production of agricultural products. Examples of an IT adoption in the agricultural fields include strategy planning, plantation and farming, logistics, storage, and marketing. Coconuts were generally classified by using Saturation (S) channel in HSV color system for inconsistence light environment [2], [3]. To improve the quality of the classification process, Density parameter (D), unaffected by the light, will be used in this study. This is because existing literature suggests that density parameter can be a potential feature for classification, even if general IF-THEN rules is applied as a classifier. In addition, color data will still be used as supportive data to enhance the quality of the classification results. Based on the knowledge of local farmers, this research provides customers an assistance on coconut selection by using an adapted stereo camera system to identify three different types of coconuts, i.e., young, mature, and old coconuts.

 Keywords: Coconut selection,stereo camera,density
Full Paper : https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8955375/
Keywords: Coconut selection,stereo camera,density
Full Paper : https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8955375/

 Keywords: Coconut selection,stereo camera,density
Full Paper : https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8955375/
Keywords: Coconut selection,stereo camera,density
Full Paper : https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8955375/
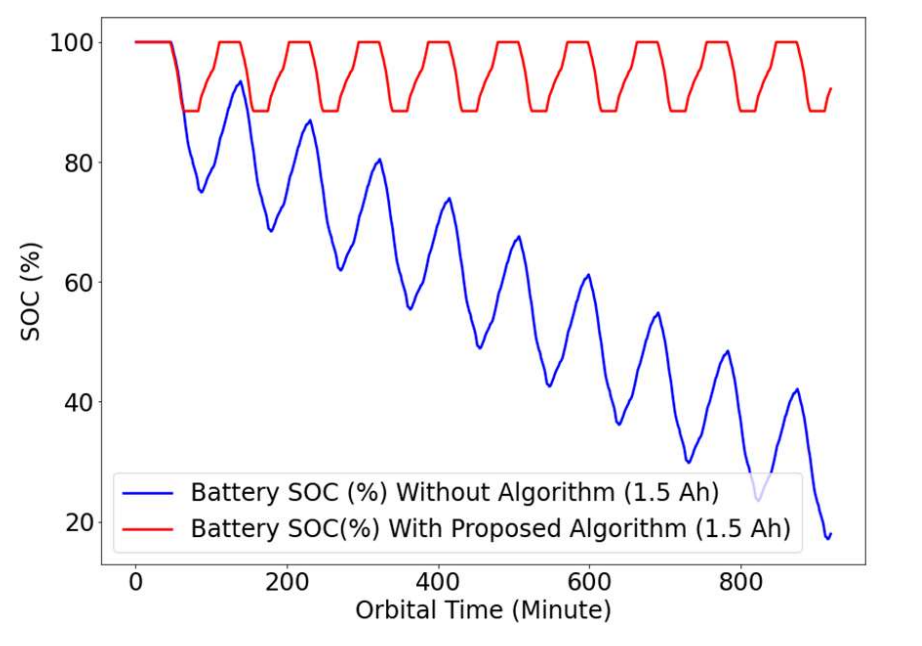
Abstract: This paper proposes the study of the lightweight dynamic algorithm of a power management for a small LEO-orbit satellite application such as CubeSat. The proposed work was designed in connection with a rule-based decision method and real-time scheduling. Here, the functional payloads of the satellite tasks were considered consisting of an electric power unit, attitude controller module, and environmental space system. The main system functions of the satellite operation were scheduled at the work process and the scheduling of the mission tasks were based on decision-making rules. It shows that the lightweight dynamic algorithm was aimed to optimize the efficiency and performance. The study of the proposed work was based on a simulation to understand the energy behavior and also consider the task priority.
The novel dynamic algorithm was proposed in order to deal with the power condition and distribution modules. It allows the strategy of a power management depending on a linear decision rule approach. The factors of power management consist of a design of the state of charge (SoC) of batteries and the consumption characteristics of the payload satellite interfaces. The energy profile was modeled according to the LEO operation based on the orbital period. The satellite payloads were concerned energy budgets including a telecommunication, attitude controller and functional loads in action. As a result, the efficiency and performance of battery can contribute to the lifespan of a satellite, and also design of a miniaturized satellite.

Keywords: dynamic algorithm; power management; small satellite


